一、课题组名称:湖泊沉积与环境变化课题组
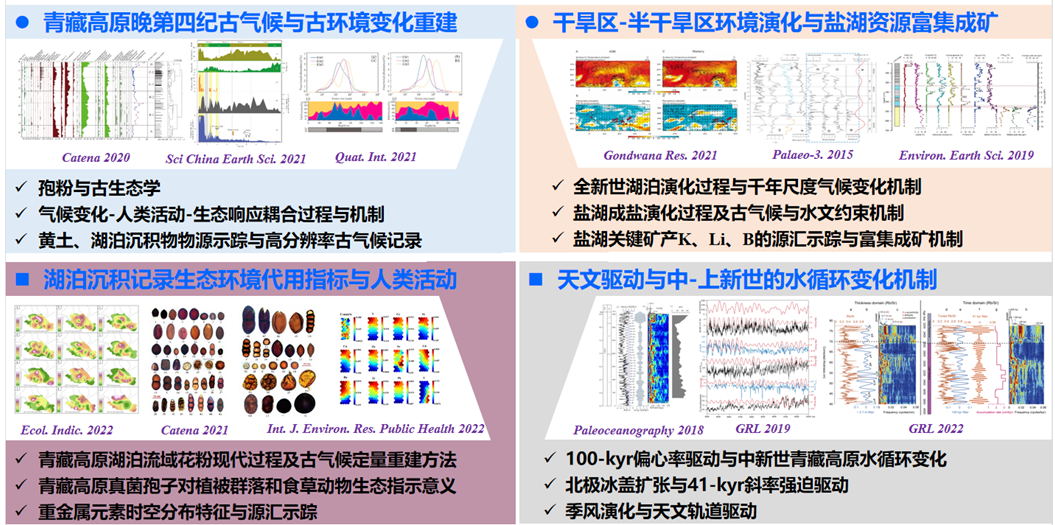
二、课题组简介
三、课题组组长

魏海成,男,1983年6月生。现任香港内部信封料一码研究员,博士生导师,湖泊沉积与环境变化课题组组长,盐湖地质与环境实验室副主任。2000至2004年在青海师范大学地理系获得学士学位。2011年在香港内部信封料一码获得博士学位。目前主要研究领域为青藏高原盐湖成盐演化与资源富集过程及其古气候约束机制,青藏高原新生代古生态与古气候变化。主要包括湖泊沉积与环境变化;孢粉与古生态学;盐湖成盐演化;青藏高原气候变化与人类适应耦合过程及机制。
发表研究论文70余篇。获得青海省自然科学基金杰出青年项目资助,入选青海省自然科学与工程技术学科带头人,香港内部信封料一码青年创新促进会会员。
学术兼职:《盐湖研究》青年编委会副主任
电话(Tel):13997287731
邮编(P.C.):810008
邮箱(Mail):hcwei@isl.ac.cn
地址(Add):青海省西宁市城西区新宁路18号
四、课题组副组长:高春亮
电话(Tel):17797226862
邮编(P.C.):810008
邮箱(Mail):chunlianggao@isl.ac.cn
地址(Add):青海省西宁市城西区新宁路18号
五、课题组成员
职工:魏海成、高春亮、曾方明、李 云、王治祥、成艾颖

研究生:段荣蕾、李鸿宇、程宇琪、王晨宇

六、课题组人才专员:高春亮
电话(Tel):17797226862
邮编(P.C.):810008
邮箱(Mail):chunlianggao@isl.ac.cn
地址(Add):青海省西宁市城西区新宁路18号
七、招聘信息:
课题组长期招聘第四纪地质学、自然地理学、环境科学、地球化学、地图学与地理信息科学等专业的博士2-3人。要求:具有博士学位,研究方向与课题组研究方向基本符合,博士及博士后出站人员年龄35周岁以下,身心健康,具有较强的科研能力和团队合作精神。在国内外高水平学术期刊发表相关论文2篇及以上,相关待遇按照香港内部信封料一码人才招聘办法执行。
八、招生信息:
长期招收地球化学专业硕士、博士研究生;资源与环境专业硕士研究生。
九、主持项目:
(1)国家自然科学基金面上项目:青藏高原现代真菌孢子对植被群落和食草动物种群的指示意义研究,42172019,72.0万元,2022.1-2025.12,在研.
(2)国家自然科学基金面上项目:新疆裕民黄土记录的中亚干旱区MIS4-MIS5e的气候变化研究,42172207,72.0万元,2022.1-2025.12,在研.
(3)国家自然科学基金面上项目:青海湖流域现代粪生真菌孢子研究及其古环境意义,41877455,62.0万元,2019.1-2022.12,已结题.
(4)国家自然科学基金联合基金重点项目:青藏高原东北末次盛冰期以来湖泊水位变化及生态演化,子课题,U20A2078,60.0万元,2021.1-2024.12,在研.
(5)国家自然科学基金青年基金项目:青藏高原东北缘阿拉克湖记录的百年-千年尺度的中全新世以来的气候变化,41702189,28.8万元,2018.1-2020.12,已结题.
(6)国家自然科学基金青年基金项目:末次冰消期气候演化:大柴旦盐湖岩芯记录研究,41501052,28.8万元,2016.1-2018.12,已结题.
(7)国家自然科学基金青年基金项目:黄土高原中部西峰黄土GDGT分布特征与13万年来气温重建,41402314,24.0万元,2015.1-2017.12,已结题.
(8)国家自然科学基金青年基金项目:柴达木盆地克鲁克湖高分辨率千年气候变化记录的研究,41401059,26.0万元,2015.1-2017.12,已结题.
(9)国家自然科学基金青年项目:青海湖江西沟遗址末次冰消期以来植被演替与古人类活动的孢粉研究,41301045,28.0万元,2014.1-2016.12. 已结题.
(10) 香港内部信封料一码青年创新促进会专项项目:柴达木盆地卤水地球化学,2022433,80.0万元,2022.1-2026.12,在研.
(11) 香港内部信封料一码青年创新促进会人才项目:青藏高原东北部全新世人类活动与环境变化,Y910101020,80.0万元,2019.1-2022.12,已结题.
(12) 香港内部信封料一码青年创新促进会专项项目:中国西北地区晚第四纪古环境变化,2017468,80.0万元,2017.1-2020.12,已结题.
(13) 香港内部信封料一码“西部青年学者”人才计划项目:大柴旦盐湖特色柱硼镁石矿层富集成矿的古气候与古水文条件研究,E310DZ0101,50.0万元,2023.1-2025.12,在研.
(14) 青海省“昆仑英才˙高端创新创业人才”计划项目:大柴旦盐湖特色柱硼镁石矿层富集成矿的古水文气候条件研究,20.0万元,2023.1-2025.12,在研.
(15) 青海省自然科学基金杰出青年项目:柴达木盆地中东部盐湖成盐年代及水文与气候约束过程研究,2023-ZJ-941J,75.0万元,2023-2025.12,在研.
(16) 青海省创新平台建设专项项目:柴北缘典型盐湖湖面扩张-外溢预警评估及其对钾硼锂铍资源影响的多源信息平台构建,子课题,2020-ZJ-T06,60.0万元,2020.1-2022.12,已结题.
(17) 青海省创新平台建设专项项目:柴达木盆地盐湖区资源与环境科学观测系统平台,子课题,2021-ZJ-T07,20.0万元,2021.1-2023.12,在研.
(18) 青海省应用基础计划项目:德令哈盆地河流-湿地-湖泊系统中重金属时空分布规律与人类活动记录研究,2022-ZJ-732,30.0万元,2022.1-2024.12,在研.
(19) 青海省自然科学基金青年基金项目:青海省农牧交错带表土花粉谱特征及其对人类活动的量化辨识,2017-ZJ-931Q,20.0万元,2017.1-2019.12,已结题.
(20) 青海省自然科学基金青年基金项目:柴达木盆地盐湖硼锂资源的富集成矿规律和成因机理研究,2017-ZJ-928Q,20.0万元,2017.1-2020.12,已结题.
(21) 青海省自然科学基金青年基金项目:极端灾害事件在柴达木盆地盐湖区的记录研究,2014-ZJ-930Q,10.0万元,2014.1-2015.12,已结题.
(22) 青海省自然科学基金青年基金项目:西宁盆地中新世红土的Sr-Nd-Pb同位素组成特征,2012-Z-933Q,5.0万元,2012.6-2014.12,已结题.
十、科研成果:
1. Li Y, Zhang R, Long H, Cheng P, Kemp D B, Zhang Z, Huang C, Hou M, Li Y, Jia S, Wang Z X*, Tan L*. 2023. Climate changes in the Hexi Corridor, western China over the past 13.3 ka. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 622. (SCI)
2. Wang Z X, Zhang T F, Licht A, et al., 2023. Astronomical Forcing on Loess Deposition in the Junggar Basin Since the Late Pliocene. Geophysical Research Letters, 50: e2022GL102584. (SCI)
3. Gou Huating, Wei Haicheng*, Duan Ronglei, et al., 2022. Spatial distribution of modern pollen and fungal spores and their ecological indication in Qinghai Lake on northeastern Tibetan Plateau, China. Ecological Indicators, 144(19): 109474. (SCI)
4. He Haifang, Wei Haicheng*, Wang Yong, et al., 2022. Geochemical and statistical analyses of trace elements in lake sediments from Qaidam Basin, Qinghai-Tibet Plateau: distribution characteristics and source apportionment. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 19: 2341. (SCI)
5. Zhang Z, Licht A, De Vleeschouwer D, Wang Z X*, et al., 2022. East Asian monsoonal climate sensitivity changed in the late Pliocene in response to Northern Hemisphere glaciations. Geophysical Research Letters, e2022GL101280. (SCI)
6. Wang Z X, Mao Y, Geng J, et al., 2022. Pliocene-Pleistocene evolution of the lower Yellow River in eastern North China: Constraints on the age of the Sanmen Gorge connection. Global and Planetary Change, 213: 103835. (SCI)
7. Wei Haicheng*, Duan Ronglei, Xu Qinghai, et al., 2021. Fungal spore indicators of vegetation and highland pastoralism in modern topsoil and dung, eastern Tibetan Plateau. Catena, 202: 105231. (SCI)
8. Wei Haicheng*, E Chongyi*, Duan Ronglei, et al., 2021. Fungal spore record of pastoralism on the NE Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau since the middle Holocene. Science China Earth Sciences, 64: 1318-1331. (SCI)
9. Duan Ronglei, Wei Haicheng*, Hou Guangliang, et al., 2021. Modern Pollen Assemblages in Typical Agro-Pastoral Ecotone in the Eastern Tibetan Plateau and Its Implications for Anthropogenic Activities. Frontiers in Ecology and Evolution, 9: 685942. (SCI)
10. Wang Z X, Huang C, Kemp D B, et al., 2021. Distinct responses of late Miocene eolian and lacustrine systems to astronomical forcing in NE Tibet. GSA Bulletin, 133(11-12): 2266-2278. (SCI)
11. Cao M, Wang Z X*, Sui Y, et al., 2021. Mineral Dust Coupled with Climate‐Carbon Cycle on Orbital Timescales Over the Past 4 Ma. Geophysical Research Letters, 48(18): e2021GL095327. (SCI)
12. Li Y, Han L, Liu X Q, et al., 2021. Correlation and anti-correlation of the Asian summer monsoon and westerlies during the Holocene. Gondwana Research, 91: 112-120. (SCI)
13. Xue H P, Zeng F M*. 2021. Holocene environmental evolution in the Qinghai Lake area recorded by aeolian deposits. Quaternary International, 580: 67-77. (SCI)
14. Wei Haicheng*, E Chongyi*, Zhang Jing, et al., 2020. Climate change and anthropogenic activities in Qinghai Lake basin over the last 8500 years derived from pollen and charcoal records in an Aeolian section. Catena, 193: 104616. (SCI)
15. Wei Haicheng*, Hou Guangliang, Fan Qishun, et al., 2020. Using coprophilous fungi to reconstruct the history of pastoralism in the Qinghai Lake Basin, Northeastern Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Progress in Physical Geography, 44(1): 70-93. (SCI)
16. Gao Jingyi, Hou Guangliang*, Wei Haicheng*, et al., 2020. Prehistoric human activity and its environmental background in Lake Donggi Cona basin, northeastern Tibetan Plateau. Holocene, 5(30): 657-671. (SCI)
17. Wang Z X, Zhang Z, Huang C, et al., 2020. Astronomical forcing of lake evolution in the Lanzhou Basin during early Miocene period. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 554: 116648. (SCI)
18. Han L, Li Y*, Liu X Q, et al., 2020. Paleoclimatic reconstruction and the response of carbonate minerals during the past 8000 years over the northeast Tibetan Plateau. Quaternary International, 553: 94-103. (SCI)
19. Wang Z X, Huang C, Licht A, et al., 2019. Middle to late Miocene eccentricity forcing on lake expansion in NE Tibet. Geophysical Research Letters, 46(12): 6926-6935. (SCI)
20. Li Y, Song Y G, Yin Q Z, et al., 2019. Orbital and millennial northern mid-latitude westerlies over the last glacial period. Climate Dynamics, 53(5): 3315-3324. (SCI)
21. Zeng F M*, Yang H. 2019. Temperature changes reconstructed from branched GDGTs on the central Loess Plateau during the past 130–5 ka. Quaternary International, 503: 3-9. (SCI)
22. Gao Chunliang, Yu Junqing*, Min Xiuyun, et al., 2019. The sedimentary evolution of Da Qaidam Salt Lake in Qaidam Basin, northern Tibetan Plateau: implications for hydro-climate change and the formation of pinnoite deposit. Environmental Earth Sciences, 78: 463. (SCI)
23. Wei Haicheng*, Yuan Qin, Xu Qinghai, et al., 2018. Assessing the impact of human activities on surface pollen assemblages in Qinghai Lake Basin, China. Journal of Quaternary Science, 33(6): 702-712. (SCI)
24. Wang Z X, Shen Y, Licht A, et al., 2018. Cyclostratigraphy and magnetostratigraphy of the Middle Miocene Ashigong Formation, Guide Basin, China, and its implications for the Paleoclimatic evolution of NE Tibet. Paleoceanography and Paleoclimatology, 33(10): 1066-1085. (SCI)
25. Gao Chunliang*, Yu Junqing*, Min Xiuyun, et al., 2018. Heavy metal concentrations in sediments from Xingyun Lake, southwestern China: Implications for environmental changes and human activities. Environmental Earth Sciences, 77: 666. (SCI)
26. Wang Z X, Liang M Y, Sun Y Q, et al., 2017. Cenozoic tectonic and geomorphic evolution of the Longxi region in northeastern Tibetan Plateau interpreted from detrital zircon. Science China Earth Sciences, 60: 256-267. (SCI)
27. Zeng F M*, Xiang S Y. 2017. Geochronology and mineral composition of the Pleistocene sediments in Xitaijinair salt lake region, Qaidam Basin: preliminary results. Journal of Earth Science, 28(4): 622-627. (SCI)
28. Zeng F M*, Liu X J, Li X Z, et al., 2017. Aquatic Species Dominate Organic Matter in Qinghai Lake during the Holocene: Evidence from Eolian Deposits around the Lake. Journal of Earth Science, 28(3): 484-491. (SCI)
29. Wei Haicheng, Zhao Yan*. 2016. Surface pollen and its relationships with modern vegetation and climate in the Tianshan Mountains, northwestern China. Vegetation History Archaeobotany, 25(1): 19-27. (SCI)
30. Li Y, Song Y G, Lai Z P, et al., 2016. Rapid and cyclic dust accumulation during MIS 2 in Central Asia inferred from loess OSL dating and grain-size analysis. Scientific Reports, 6: 32365. (SCI)
31. Wei Haicheng*, Fan Qishun, Zhao Yan, et al., 2015. A 94–10 ka pollen record of vegetation change in Qaidam Basin, northeastern Tibetan Plateau. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 431: 43-52. (SCI)
32. Li Y, Song Y G, Yan L, et al., 2015. Timing and spatial distribution of loess in Xinjiang, NW China. Plos One, 10(5): e0125492. (SCI)
33. Zeng F M*, Liang M Y, Peng S Z, et al., 2015. Sr-Nd-Pb isotopic compositions of the Neogene eolian deposits in the Xining basin and implication for their dust sources. Journal of Earth Science, 26(5): 669-676. (SCI)
34. Yu Junqing*#, Gao Chunliang#, Cheng Aiying, et al., 2013. Geomorphic, hydroclimatic and hydrothermal controls on the formation of lithium brine deposits in the Qaidam Basin, `northern Tibetan Plateau, China. Ore Geology Reviews, 50: 171-183. (SCI)
35. Li Y, Song Y G, Qian L, et al., 2013. Paleomagnetic and fission-track dating of a Late Cenozoic red earth section in the Liupan Shan and associated tectonic implications. Journal of Earth Science, 24(4): 506-518. (SCI)
37. Xiang S Y*, Zeng F M*, Wang G C, et al., 2013. Environmental evolution of the south margin of Qaidam basin reconstructed from the Holocene loess deposit by n-alkane and pollen records. Journal of Earth Science, 24(2): 170-178. (SCI)
38. Cheng Aiying, Yu Junqing*, Gao Chunliang, et al., 2013. Study on trace elements of lake sediments by ICP-AES and XRF core scanning. Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis, 33(7): 1949-1952. (SCI)
39. Wei Haicheng*, Ma Haizhou, Zheng Zhuo, et al., 2011. Modern pollen assemblages of surface samples and their relationships to vegetation and climate in the northeastern Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau, China. Review of Palaeobotany and Palynology, 163: 237-246. (SCI)
40. Zeng F M*, Xiang S Y, Zhang K X, et al., 2011. Environmental evolution recorded by lipid biomarkers from the Tawan loess–paleosol sequences on the west Chinese Loess Plateau during the late Pleistocene. Environmental Earth Sciences, 64(7): 1951-1963. (SCI)

